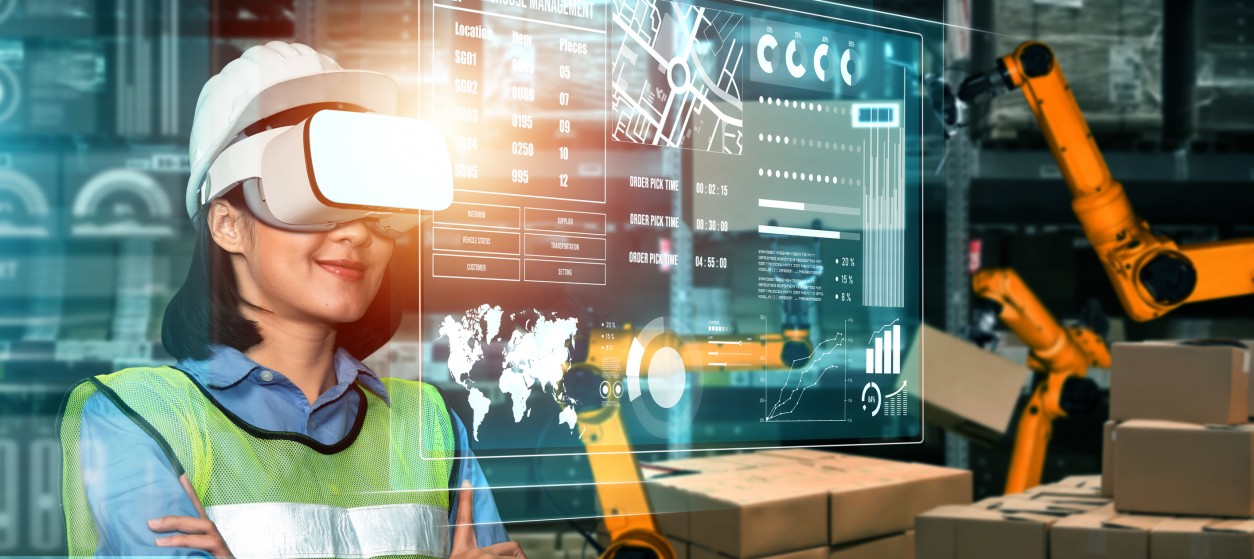
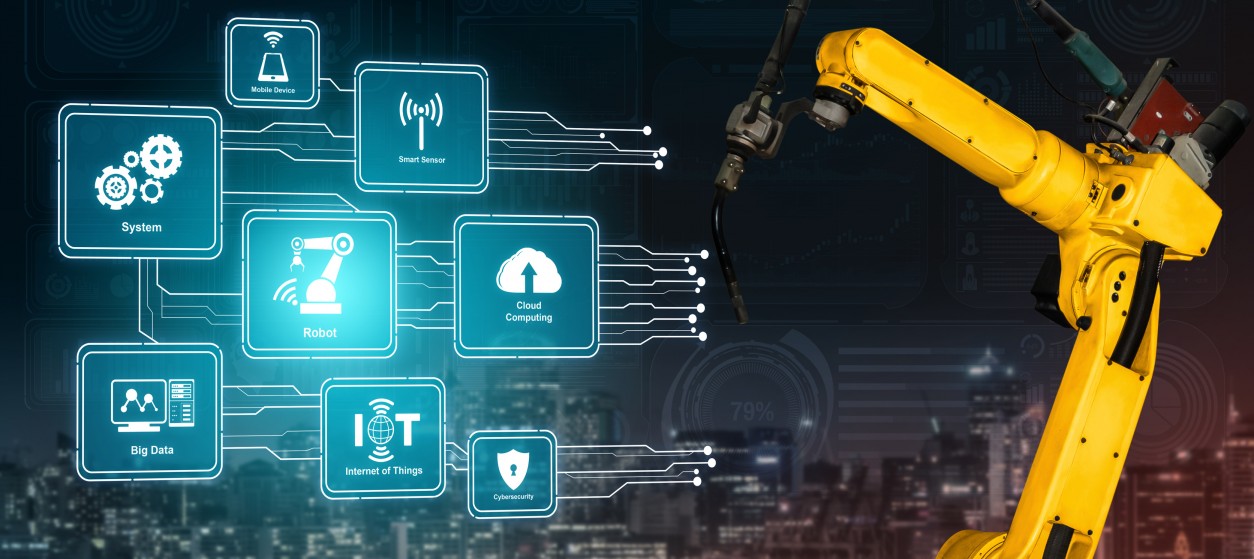
Industry 4.0 is described as the fourth industrial revolution and is a wide concept that ranges from smart manufacturing to data mining, robotics, and artificial intelligence. Industry 4.0 refers to the digitization of the manufacturing industry, making use of a wide array of information technologies to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of production through the integration with Information Technology (IT), cloud computing, and various information services. The term Industry 4.0 was originally invented by German industry associations, which used it to describe the digital transformation of manufacturing enterprises. Over the years, Industry 4.0 has evolved to a wider strategic approach to the development of digitally enabled factories and their interconnection as part of manufacturing value chains. As such it jointly addresses a set of goals and objectives in the context of business and economic policy, while enabling the establishment of entire ecosystems and networks of business partners. Such Industry 4.0 ecosystems are formed all around the globe and are gradually changing the way enterprises perceive manufacturing, organizing large-scale production systems, influencing the range of manufacturing designs, and are ultimately reshaping global value chains and markets. From a practical perspective, the establishment of partner ecosystems in the Industry 4.0 era is based on the deployment of cutting-edge digital technologies i.e. the “digital enablers” of the fourth industrial revolution and of the operation of smart factories.
Enablers of Industry 4.0
The core Industry 4.0 technologies include cloud computing, edge computing, Internet of Things (IoT), big data and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies are interrelated, with each one complementing the other to create an intelligent enterprise ecosystem that can monitor its environment and take action to optimize production processes in real-time. Specifically, the main digital enablers of the industrial revolution 4.0 are:
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing is a technology that allows manufacturing enterprises to securely store, access, and transfer data from anywhere on the internet and without essential limitations in capacity and quality of service. Industry 4.0 enterprises can therefore transfer and process large volumes of physical data in the cloud. Moreover, a cloud infrastructure can host data and services from multiple enterprises of an Industry 4.0 value chain. Hence, the cloud facilitates trusted sharing of data and services across entire ecosystems of business partners.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing complements cloud computing by enabling access, sharing, and processing of data in a manufacturer’s local area network. This obviates the need for transferring all the data to a remote cloud (i.e., through a wide area network), especially in cases where real-time performance is required or when data are sensitive and should not be shared to the cloud. Overall, edge computing enables manufacturers to collect and analyze data at the edge of a network, which allows for quicker responses to events, reduces bandwidth demands, and results in fewer CO2 emissions.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The Internet of Things (IoT) enables manufacturers to collect and analyze data from the millions of internet-connected devices that are deployed in modern factories. Thanks to sensors, RFID tags, automation devices (e.g., Programmable Logic Controllers), and more complex smart objects like drones and industrial robots, Industry 4.0 partner ecosystems can collect and exchange data over a network without human assistance. This leads to an incredible amount of Big Data being created daily. Most importantly, internet-connected objects enable modern factories to automatically execute automation processes, including shopfloor processes like picking, packing, welding, and quality inspection. Nowadays these processes can be carried out without human intervention i.e., with the human in a supervisory role only.
- Big Data: In general, Big Data refers to large amounts of complex data sets that can only be processed with specialized tools. Big Data processes are very useful for manufacturing enterprises because they can help them extract insights and take data-driven decisions about optimizing their production processes. In the context of an Industry 4.0 value chain, Big Data technologies can also help businesses find patterns and trends in their customers’ behavior to improve production processes and supply chain operations as a result.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is another key component of Industry 4.0 technology that collects endows automation systems with human-like capabilities from detecting faulty products to performing shopfloor operations. AI in manufacturing comes in different flavors that range from machine learning in processes like predictive maintenance and quality management, to human-robot collaboration on the shopfloor.
Industry 4.0 Use Cases
The above-listed digital components and technologies, enable Industry 4.0 partner ecosystems to implement a wide range of value-added use cases. Prominent examples include:
- Flexible Manufacturing: Flexible manufacturing involves implementing technologies and processes that can easily adapt to meet changing customer needs. In most flexible manufacturing scenarios, the focus is on speed, agility, and flexibility. While the third industrial revolution was mainly about effective mass production (i.e. products made to stock), Industry 4.0 is realizing a shift towards mass customization (i.e. products made to order). Industry 4.0 partner’s ecosystems are therefore able to create personalized products that are tailored to the customers’ needs.
- Predictive maintenance: In predictive maintenance, machine sensors continuously send data to a central location where it’s analyzed for early detection of component failures or safety issues. This allows maintenance to be scheduled before actual problems arise, minimizing downtime and maximizing efficiency. Leveraging predictive maintenance systems, Industry 4.0 value chain participants can maximize their Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE), which has a positive impact on the efficiency of supply chain operations as well.
- Quality Management: Industry 4.0 partners are provided with unprecedented opportunities to proactively detect and anticipate quality problems in their production. In this direction, predictive quality management uses Internet of Things (IoT) data gathered at various points in the production process to detect and resolve quality issues in real-time. This enables manufacturers to identify and fix problems before they become serious enough to affect a customer’s experience with the product.
- Digital Twins: Digital twins are virtual models of physical systems used for testing and simulation purposes. These models can be used to troubleshoot potential problems, optimize system performance and determine the best way to integrate new technologies, among other things. In the scope of an Industry 4.0 partner ecosystem, business partners can also create a digital twin of their supply chain to experiment with the efficiency of supply chain operations under different scenarios.
Industry 4.0 Value Chains and Ecosystems Transformation
A value chain is a set of activities that a firm operating in a specific industry performs in order to deliver a valuable product or service for the market. In Industry 4.0, the value chain continues to be an important element of reference, albeit it is now extended throughout the whole connected ecosystem of actors involved in delivering the final product or service to customers. The main characteristic of the industry 4.0 value chains is the trusted and interoperable exchange of information between different actors (customers, suppliers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), MROs (Maintenance and Repair Operations), etc.) in order to improve design and manufacturing processes and reduce time-to-market. This kind of value chain is enabled through interconnected smart devices with digital capabilities gathering data from different physical sources (i.e., machine to machine communications) and feeding them into various software solutions that can manage, analyze, process and transform them into valuable insights for all actors involved in the production cycle. Overall, Industry 4.0 value chains and partner ecosystems differ from legacy supply chains due to their following characteristics:
- Connected: Contrary to legacy manufacturing systems, machines and devices in Industry 4.0 value chains are connected among each other to enable a trusted and interoperable exchange of information between different actors in the industry.
- Decentralized decision-making: Each actor in an Industry 4.0 chain (e.g., machine, worker, device) takes local decisions based on their knowledge and awareness of the global context, which maximizes efficiency.
- Cyber-physical systems: Industry 4.0 value chains leverage systems with high autonomy, which combine real-world and virtual world through sensors and actuators.
- Collaborative: Actors in the Industry 4.0 value chain tend to collaborate with each other to achieve a common goal. This is possible thanks to their interconnection and context awareness characteristics.
To sum up, Industry 4.0 partner ecosystems bring together a variety of stakeholders to produce new opportunities and develop innovative solutions based on novel digital application platforms. During the next decade, Industry 4.0 will usher in a new model of development that opens broad possibilities for actors who want to create industrial and economic change as part of their digital transformation strategy. Nevertheless, even though Industry 4.0 creates many opportunities, it also poses challenges for some industries because the rate of innovation often exceeds their companies’ ability to adapt. Regardless, Industry 4.0 is poised to change how businesses operate across all industries and countries, bringing more efficiency and better products to the marketplace everywhere. This is the reason why modern enterprises cannot afford to ignore Industry 4.0 value chain but should rather strive to become part of them the soonest possible.